
Motor vehicle crashes are the leading cause of death for children and youth older than 4 years. Each year, more than 5000 children and adolescents under the age of 21 years die in crashes. For every death, approximately 18 children are hospitalized and more than 400 receive medical treatment of injuries sustained in a crash.
Car safety seats have been shown to be very effective at preventing death and serious injury for our youngest children. Over the past decades, car seat technology has steadily improved in safety and ease-of-use features and provided higher weight and length limits at each stage.
However, these lifesaving and readily available devices are too often misused or not used at all. Reports show 3 out of 4 car safety seats are misused (Cite). The CDC reported in 2019 of the children who died in a crash, 41% of 4–7-year-olds and 27% of children less than 4 years old were unrestrained.
Since parents view their children’s doctors as a reliable source for safety advice, pediatricians can be a huge part of the solution to this nationwide problem. Explore the AAP policy statement and technical report for more guidance on car safety seats including an algorithm to guide implementation of best practice recommendations of car safety seats.
Using the correct car seat can safe a child’s life:
Once a child has outgrown the height and weight limits of a rear facing car safety seat, they should be transitioned to a forward-facing car safety seat with a harness for as long as possible, up the highest weight and height allowed by their car safety seat.


Once a child has outgrown the height and weight limits of a rear facing car safety seat, they should be transitioned to a forward-facing car safety seat with a harness for as long as possible, up the highest weight and height allowed by their car safety seat.
Once a child has outgrown the front facing convertible safety seat, they should use a belt-positioning booster seat until the vehicle seat belt fits properly. Typically when they have reached 4 ft 9 inches in height and are between 8-12 years of age.

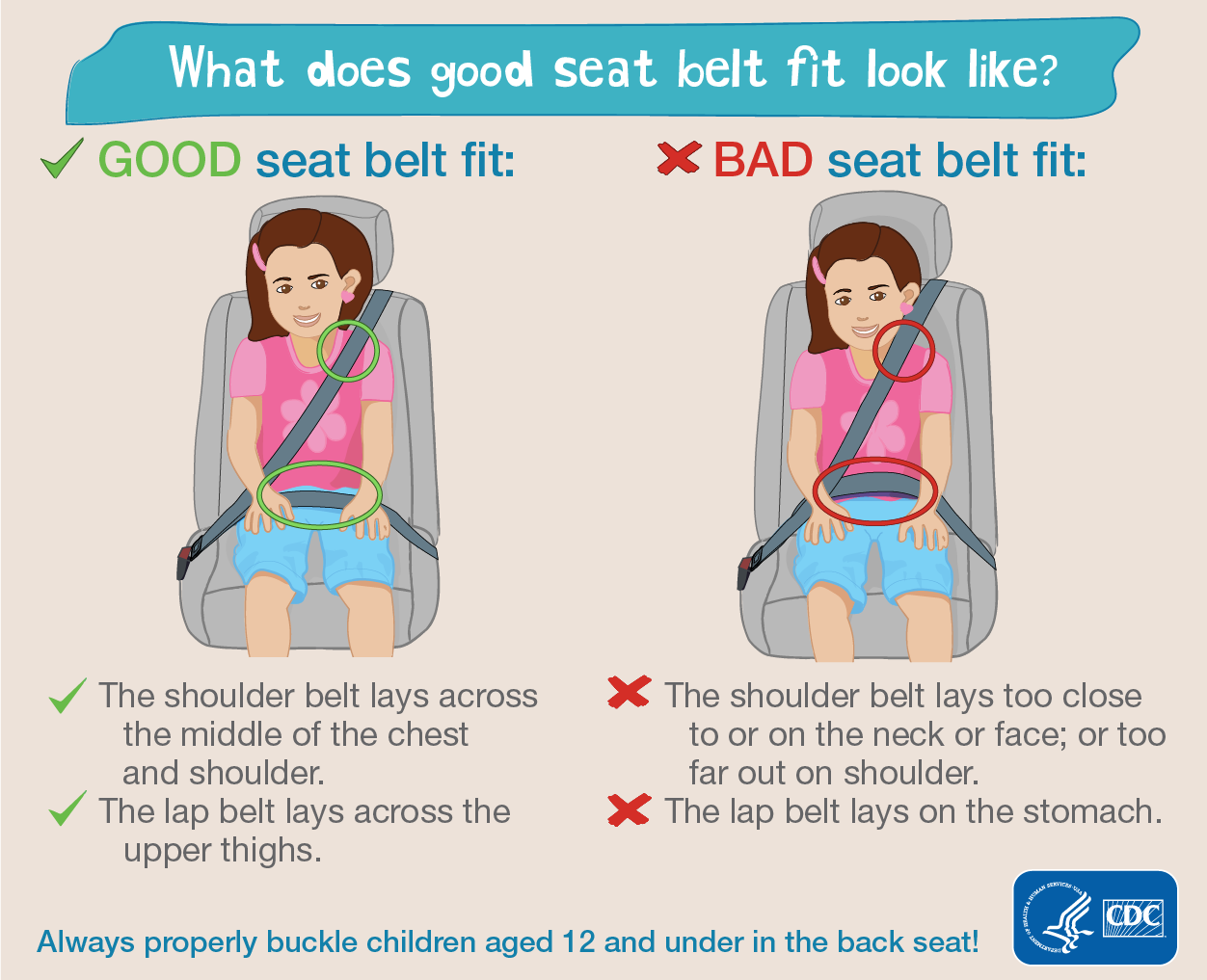
All children less than 13 years old should be restrained in the rear seats of vehicles for optimal protection. When children are large enough and old enough to use the vehicle seat belt alone, they should always use lap and shoulder seat belts for optimal protection.
There are many opportunities during a well child visit that child passenger safety could be discussed.
A certified child passenger safety technician can be an important community partner. Find out if any are employed by your medical facility. If so, are they available to talk to families or provide consultations? Do they have special needs training? If you don’t have a certified technician available, you can locate one near to you by visiting cert.safekids.org.